Is there a magic pill that can enhance your brain? Could magnesium be the secret to boosting brainpower? How effective is magnesium for your brain anyway?
To begin with, it’s no secret that magnesium is a vital nutrient. From building strong bones to producing energy and proteins, and even keeping your heart beating, magnesium contributes to over 600 biochemical functions in the body. 1
But there’s more to magnesium than just these fundamental roles. Studies show that magnesium can also improve your memory and learning ability. On the flip side, a deficiency in magnesium can significantly impair these cognitive functions.2
Table of Contents
How does magnesium help with learning?
Magnesium is crucial for brain health because it supports the process of brain plasticity. 3 Brain plasticity is the brain’s ability to form new connections between neurons, which is essential for learning and memory.
Research has shown that magnesium enhances brain plasticity by promoting the growth and connection of brain cells. In experiments, brain cells grown in a petri dish formed connections more effectively in the presence of magnesium. This improved connectivity makes it easier to learn, think, memorize, and develop positive behavior patterns. 4
Is there a form of magnesium that can cross the blood-brain barrier?
Most standard oral magnesium supplements cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, a protective membrane that separates the brain from the blood. This means they cannot increase magnesium levels in the brain.
The good news is that a group of international researchers from MIT, Tsinghua University (Beijing), and the University of Toronto developed a new type of magnesium called Magnesium-L-Threonate, branded as Magtein®. This form of magnesium can pass the blood-brain barrier and can be taken as a capsule, effectively raising brain magnesium levels. 5
Researchers initially tested Magtein® on rats, finding it enhanced their learning abilities and improved both short- and long-term memory. 6 Human studies reported similar results: healthy Chinese adults showed significant memory improvements, with older participants experiencing the most improvement.7
At Intelligent Labs, each serving of our MagEnhance Triple Magnesium Complex contains 1,000 mg of Magtein® Magnesium-L-Threonate. This formulation helps boost brain magnesium levels and supports cognitive function.

How does Magnesium L-Threonate boost brainpower?
Ready for a bit of a deep dive into the science? Stay with us – this is where we explain the real ‘magic’ behind Magnesium L-Threonate and why it’s such a game-changer for cognitive function. The image on the right will help you follow along.
So, magnesium interacts with the NMDA receptor, which is crucial for learning. This receptor is found in the gap (synapse) between nerve cells (neurons).
The NMDA receptor gets activated by the neurotransmitter glutamate. This activation allows calcium to flow through the channel, sending electrical signals between neurons.
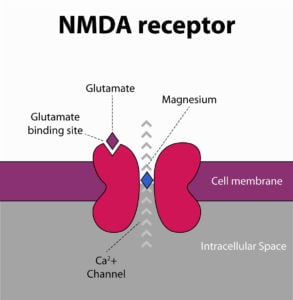
Magnesium can stop glutamate from activating the NMDA receptor. By doing this, it “closes” the door, preventing calcium from flowing through the channel. Essentially, magnesium acts like a “guard,” preventing too much glutamate from activating these receptors and preventing overstimulation of the neuron.
When neurons are overstimulated, they don’t fire their impulses normally. The electrical signals or connections they try to make are often unsuccessful. Imagine a huge crowd of people all trying to push through a turnstile at once—it just doesn’t work. Without magnesium acting as a guard, prolonged overstimulation can damage nerve cells. This can lead to problems with learning and memory over time.8
This protective role of magnesium also explains why it helps with headaches and migraines. By relaxing blood vessels and regulating neurotransmitters involved in migraine attacks, studies have shown that magnesium can reduce the frequency and severity of these debilitating headaches. 9 10
Aside from boosting brainpower, how else can magnesium help?
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral with numerous benefits beyond enhancing cognitive function. At Intelligent Labs, we’ve formulated MagEnhance Triple Magnesium Complex to support various aspects of your health.
MagEnhance includes three distinct forms of magnesium, each chosen for its unique properties:
Magnesium-L-Threonate: As you’ve learned in this blog, this form is specifically designed to cross the blood-brain barrier. It helps improve memory and learning abilities by increasing brain magnesium levels.
Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its high bioavailability, this form is gentle on the stomach and effectively addresses magnesium deficiencies throughout the body.
Magnesium Taurate: This type combines magnesium with taurine, providing a calming effect that helps reduce stress and enhance sleep quality.
Together, these forms of magnesium in MagEnhance not only support brain health but also contribute to better sleep, reduced stress, and improved overall bodily functions.
Want to learn more about the differences between these forms? Check our detailed blog post here: Magnesium Glycinate vs. L-Threonate vs. Taurate: What’s the Difference?
💬 Something on your mind? Share your thoughts in the comments. We love hearing from curious minds.
📩 And while you’re here, join our newsletter for more smart stuff (and secret perks)!
References:
- de Baaij, Jeroen H F et al. “Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease.” Physiological reviews vol. 95,1 (2015): 1-46. doi:10.1152/physrev.00012.2014 ↩︎
- Slutsky, Inna, et al. “Enhancement of Learning and Memory by Elevating Brain Magnesium.” Neuron, vol. 65, no. 2, Jan. 2010, pp. 165–177, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.12.026. ↩︎
- Liao, Wang, et al. “Magnesium Elevation Promotes Neuronal Differentiation While Suppressing Glial Differentiation of Primary Cultured Adult Mouse Neural Progenitor Cells through ERK/CREB Activation.” Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 11, 23 Feb. 2017, pp. 87–87, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00087 ↩︎
- Puderbaugh, Matt, and Prabhu D. Emmady. “Neuroplasticity.” PubMed, StatPearls Publishing, 2022, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557811. ↩︎
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. “PubChem Compound Summary for CID 45489777, Magnesium L-Threonate” PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Magnesium-L-Threonate. ↩︎
- “Science.” Magtein.com, magtein.com/science/ ↩︎
- Zhang, Chengxiang et al. “A Magtein®, Magnesium L-Threonate, -Based Formula Improves Brain Cognitive Functions in Healthy Chinese Adults.” Nutrients vol. 14,24 5235. 8 Dec. 2022, doi:10.3390/nu14245235 ↩︎
- Ruppersberg, J. Peter, et al. “The Mechanism of Magnesium Block of NMDA Receptors.” Seminars in Neuroscience, vol. 6, no. 2, 1 Apr. 1994, pp. 87–96, https://doi.org/10.1006/smns.1994.1012 ↩︎
- Yablon, Lisa A., and Alexander Mauskop. “Magnesium in Headache.” PubMed, University of Adelaide Press, 2011, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507271/. ↩︎
- Domitrz, Izabela, and Joanna Cegielska. “Magnesium as an Important Factor in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Migraine—from Theory to Practice.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 5, 5 Mar. 2022, p. 1089, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051089. ↩︎